How will space robotics market gain traction with the rising number of contributions by prominent industry stakeholders?
Publisher : Fractovia | Published Date : 2019-05-06Request Sample
Rising enterprise and government spending towards development of space exploration technologies has propelled the space robotics market revenues, as efforts are being made to bring more efficiency into activities like equipment maintenance, satellite assembly and extraterrestrial surveys. Essentially, performing physical tasks in the orbit not only present risks for astronauts, but also require high levels of precision and control. Robotic arms or manipulator systems can provide the necessary accuracy and automation to safely repair and maintain spatial objects. Continuous improvement of automated systems and the ability of robots to significantly increase productivity will fuel the space robotics industry expansion.
China space robotics market, by application, 2019 & 2025 (USD Million)
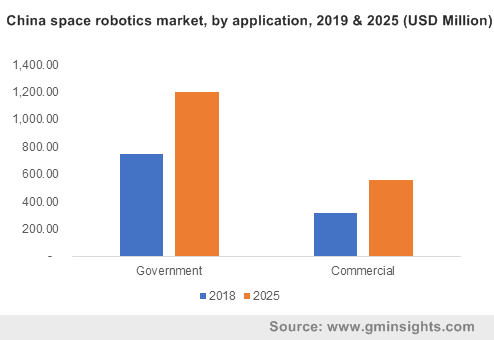
Over the past few years, thousands of satellites have been launched into earth’s orbit, while aerospace companies have attempted to realize commercial space flights and make them affordable. All the while, governments are funding projects to explore interplanetary surfaces, the most notable being Mars exploration. The space robotics market can be pegged as a vital component of these projects, since equipment like rovers and probes are valuable in investigating surfaces and collecting samples using robot arms. Activities like placing a satellite into orbit, collecting and providing information on space aircraft functions and assisting flight crew in handling spatial objects can be done cost-effectively and without delays by using robotic equipment.
Apparently, the space robotics market is poised to witness considerable growth in the imminent future owing to increased venture capital funding into space application-oriented start-ups, along with huge investment by technology giants into developing their own equipment, software and services. Reports indicate that in 2018, nearly USD 2.97 billion equity capital had been invested in space companies worldwide. One can certainly expect a large number of viable space technologies to be unveiled and commercialized over the coming years, further creating opportunities for the space robotics industry.
A brief overview of the competitive spectrum of the space robotics market:
Motiv Space Systems
California-based Motive Space Systems, a provider of aeronautics solutions, was selected by NASA to develop the robotic arms for spacecraft to be used in the upcoming Mars 2020 mission, under a multi-million dollar agreement. Being the most crucial part of the mission, the arms would be more advanced and stronger than the previous rover sent to Mars. The project signifies a massive potential for the space robotics market from surface exploration missions, as several countries, including China and Russia would also be looking to launch similar projects, with robotic arms being an indispensable component of space rovers and aircrafts.
Maxar Technologies
Presenting a technological offering that has widespread commercial applications, Maxar Technologies is in the process of completing its Dragonfly project, which is another NASA program, aimed at assembling spacecraft parts in the orbit. The program would make it possible to launch antennas and other satellite systems in a more compact way inside a rocket. Dragonfly, supposedly a robotic arm weighing 76 Kgs and capable of reaching 5 meters from the bases, would be having motors, avionics and advanced sensors to eliminate the single point of failure risk. Maxar is planning to offer the program as a commercial offering to private satellite operators as well as government agencies, which will immensely transform the approach of the space robotics industry.
Orbital ATK
On the verge of providing a novel and possibly revolutionary service to commercial operators of geostationary satellites, Orbital ATK had last year confirmed its plans to develop the Mission Robotic Vehicle (MRV) and the Mission Extension Pods (MEP). The MRV and MEP would be used to handle the station-keeping of geo satellites, especially those soon to be out of fuel. Reportedly, the MRV would get close to a satellite and using a robotic arm will attach to it the MEP, that will handle its upkeep and extend its life by up to 5 years. The service will help communication companies expand their geo-sat’s life and save incredible amount of money, in addition to safely disposing them into the graveyard orbit when needed.
In a nutshell, the space robotics industry is gradually expanding in terms of commercial applications, as launching and maintaining satellites is crucial for the global communications industry which provides connectivity, entertainment and geospatial mapping services. Touted to progress significantly through strategic collaborations between the public and the private sectors, the space robotics market is projected to surpass annual revenues of USD 3.5 billion by 2025.