U.S. atrial fibrillation drugs market to amass substantial proceeds by 2025, rising awareness trends & the urgent need for preventive measures to augment the global industry outlook
Publisher : Fractovia | Published Date : 2019-05-30Request Sample
Atrial fibrillation, being one of the most common types of heart arrhythmia, affects a large portion of population. Atrial fibrillation drugs market has recorded increased traction predominantly due to the influx of “baby boomers” and forecast for an atrial fibrillation epidemic within the next 10 to 20 years. Though various studies disagree with the prediction of an atrial fibrillation endemic, it cannot be denied that the prevalence of the condition is on the rise and a significant amount of health resources are invested in detecting and managing atrial fibrillation.
U.S. Atrial Fibrillation Drugs Market, By Product, 2018 & 2025 (USD Million)
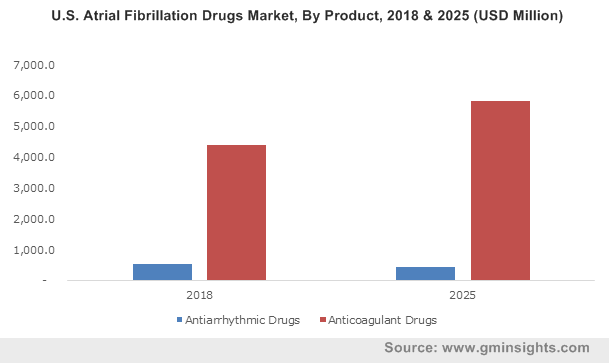
Multiple large observational cohort studies have conclusively established the consequences of atrial fibrillation and have shown that chances of systemic embolism and stroke increase if no oral anticoagulation is taken, leading to increase of morbidity and mortality. Considering the medical burden of atrial fibrillation, methods for detection, prevention and controlling atrial fibrillation have been improved which has imparted a significant boost to the atrial fibrillation drugs market, a trend projected to continue over 2019-2025.
According to the American Heart Association 2.7 million Americans are living with atrial fibrillation. Other sources predict that as the global population continues to age, the number will increase to 6 to 12 million in the USA by 2050 and 17.9 million in Europe by 2060. Though the reasons for the prevalence of atrial fibrillation remain elusive, according to the World Heart Federation atrial fibrillation utilizes significant health resources globally. The CDC estimated that yearly, more than 750,000 hospitalizations occur due to atrial fibrillation and the condition contributes to nearly 130,000 deaths each year. Atrial fibrillation costs the U.S. approximately $6 billion with medical costs amounting to almost $8,705 higher per year for people affected by atrial fibrillation than for people who do not have atrial fibrillation.
Such factors together have acted as a potent boost for the atrial fibrillation drugs industry as the condition, when remedied with medication can substantially reduce the risk of a stroke or clot. For long, blood thinners had been recommended by doctors for the prevention of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation but Warfarin, once the drug of choice for atrial fibrillation is losing its place to NOACs or non-vitamin K oral anticoagulant. This is mainly because warfarin came with the inherent risk of severe bleeding and therefore frequent lab tests and checkups were a mandate to ensure patients have the right dose.
Clinical trials showed that the newer blood thinners caused less bleeding risk and some of them are even better at preventing blood clots and stoke. In case patients do develop severe bleeding or need emergency surgery, the effects of NOACs are more easily reversed than that of warfarin, as reversal agents can work within hours to halt anti-clotting activity of NOACs compared to the entire day or more – which is the time frame required to reverse the effects of warfarin. Increased investments in research and development in the atrial fibrillation drugs industry have potentially attributed to the development of such newer forms of atrial fibrillation medications that have substantially helped patients in need.
Studies to evaluate the use of direct-acting oral anticoagulants have been increasing in nursing home residents ever since their introduction. Nursing homes necessarily house the greatest number of residents at the risk of atrial fibrillation. Therefore the rise of anticoagulant use among nursing home patients is a positive indicator for the increased scope of the atrial fibrillation drugs market.
Global burden of atrial fibrillation varies between regions with the prevalence and incidence of atrial fibrillation being higher in high-income countries when compared to low-middle income countries. However experts caution that this difference in extent of atrial fibrillation in developing countries and developed countries can be in part attributed to the limited access to health care and under reporting the actual number of cases due to the disparity in published data.
Still, the atrial fibrillation drugs market in developed nations like the U.S. is arguably one of the largest in the world due to the fact that patients in developed countries have better access to healthcare services and are therefore not only aware of conditions like atrial fibrillation but also undergo timely diagnosis and medication which makes the atrial fibrillation drugs industry much more expansive in such countries. For instance, the U.S. atrial fibrillation drugs market is expected to witness a CAGR of 2.4% over 2019-2025 due to rising venture capital investments by manufacturing firms, increasing geriatric population and growing adoption of new pharmaceutical drugs.
With global awareness about atrial fibrillation and the importance of preventing atrial fibrillation with medication on the rise, it is expected that the trend witnessed in developed countries will be extended to developing countries as well. The would consequently expand the growth scope for atrial fibrillation drugs market that is slated to amass substantial proceeds over 2019-2025.